how to draw 3d structures
Introduction to Lewis Structures
The only thing smaller than atoms are their subatomic particles; electrons, protons, and neutrons. Not fifty-fifty under a complex microscopic can nosotros view the individual electrons that surround an atom's nuclei. The Lewis Dot Structure is a visual which represents the outermost beat of electrons, also known equally valence electrons, and possible covalent bonds within an atom or molecule. These valence electrons are negatively charged and are attracted to the positively charged nucleus, made up of neutrons and protons. Continue in mind that in reality electrons are constantly moving around the nucleus and are not rooted in i place as portrayed in a 2d construction.
A Lewis Dot Structure is fatigued by a serial of dots, lines, and diminutive symbols and provides a structure for the manner that the cantlet or molecule is arranged. A Lewis Dot Construction can exist made for a single atom, a covalent compound, or a polyatomic ion.
Using the Periodic Tabular array to Depict Lewis Dot Structures
The periodic table has all of the information needed to draw a Lewis dot construction. Each Group, or column, is indicated past a roman numeral which represents the number of valence electrons. This is applicable to the entire group. For example, all elements which fall within the first column, or Group I, has one (1) valence electron. All elements in Grouping 2 have two (2) valence electrons, all the mode up to VIII, eight (8) valence electrons. Properties are as well consistent across the rows, or periods, of the periodic table. Periods are indicated past a number, 1, 2, 3, etc. which correspond the free energy level, or trounce of electrons. The showtime catamenia, or row, has but one free energy level that can agree a full of ii electrons. Period ii, with a second shell, tin concord a total of viii (8) electrons, also known as the octet rule. Catamenia 3 so along tin can hold more than eight (eight) electrons.
The periodic table also conveys electronegativity. The almost electronegative elements are located in the uppermost correct corner of the period tabular array and decrease in electronegativity as you go downwardly the Grouping or more than left of a Period.
Throughout cartoon Lewis dot structures, the periodic table will be a strong reference signal when working with electrons, covalent bonding, and polyatomic ions.
Using Lewis Dot Structures to Evidence Valence Electrons
Lewis dot structures can be fatigued to show the valence electrons that surroundings an atom itself. This type of Lewis dot structure is represented by an diminutive symbol and a serial of dots. Run into the following examples for how to draw Lewis dot structures for common atoms involved in covalent bonding.
Example 1. Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for the Hydrogen cantlet.
Since Hydrogen is in Group I it has i (1) valence electron in its shell.

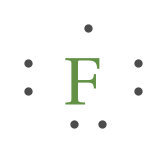
Example 2. Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for the Florine atom.
Since Fluorine is in Period ii, it can fit a maximum of eight (8) electrons 2d energy level. Fluorine Group VII, which ways it has a total of vii (7) valence electrons around the atom.
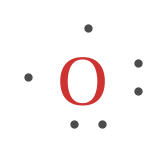
Example three. Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Oxygen.
Since Oxygen is in Period two, information technology can fit a maximum of 8 (viii) electrons 2d energy level. Oxygen Group VI, which ways it has a total of six (6) valence electrons around the atom
Example A. Decide the total number of valence electrons for C
- Carbon is in Grouping Four, 4 valence electrons
- Total # of Valence Electrons in Carbon = iv
Example B. Determine the full number of valence electrons for HtwoO
- Hydrogen, Group I, has 1 electron ten ii = two
- Oxygen, Group Half dozen, has half dozen electrons ten one = vi
- Total Valence Electrons in water = eight
Example C. Make up one's mind the total number of valence electrons for MgBrtwo
- Magnesium, Group two, has two electrons x ane = 2
- Bromine, Group vii, has seven electrons ten 2 = 14
- Total # of Valence Electrons in MgBr2 = xvi
How to Draw a Lewis Dot Structure
Step 1. Decide the full number of valence electrons to be depicted in the Lewis diagram.
Example: COtwo Total = 16
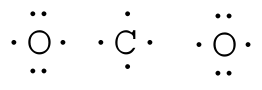
Pace 2. Place least electronegative element in center and depict single bonds from the central atom to other atoms.
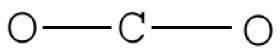
Step 3. Determine how many electrons must be added to central element.
Presume that each outer element has a total valence (2 for H, 8 for everything else) from bonding and non-bonding electrons. Total all of these electrons, and subtract that from the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. CO2 has 16 valence electrons. We assume each O has 8 valence electrons. ii×8=16; 16-xvi=0 therefore we don't need to add any electrons to C
Step 4. Add double or triple bonds to primal cantlet until it has a full octet

Step 5. Add electrons to outer elements until they accept full octets
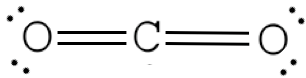
Examples for Cartoon Lewis Dot Construction for Covalent Bonds
Here, we will be using the determined total number of valence electrons per atom and drawing them in the proper places. Reference the "How to Draw a Lewis Dot Structure" for a Step past Step guide. Meet the following Lewis dot structure diagrams for a few covalent compounds.
Example ane. Ammonia, NHiii
Nitrogen is in Group Five which means information technology has a full of five (five) valence electrons. There are three (three) hydrogens nowadays, each with their own sole electron giving the entire molecule a full of 8 (8) to exist accounted for. Since Nitrogen has v electrons and is looking for a full of 8 to fulfill its second free energy shell, information technology is satisfied by the presence of 3 hydrogens which fulfills the octet rule. A nonbonding pair of Nitrogen is left and represented a pair of 2 dots.

Case two. Methane, CH4
In this structure, there are no nonbonding pairs of electrons present. All have been properly bonded in a serial of lines representing 2 electrons each. In marsh gas, each Hydrogen has the beginning free energy shell filled with 2 electrons, its own valence electron along with a shared electron from Carbon, and Carbon'south 2d free energy shell is filled with a total of 8 electrons, 4 of its own and 4 shared (1 from each Hydrogen surrounding information technology).

Drawing Lewis Dot Structures for Polyatomic Ions
Lewis Dot Structures for cartoon polyatomic ions are done very similarly to that of drawing individual atoms or covalent compounds. However, in this case, we will be dealing with ions rather than elementary atoms. Ions are going to possess either a positive or negative accuse which should be reflected past the number of electrons drawn as well every bit an indication of a "-"or "+". This means that in that location are either additional electrons present to create a negative charge or less electrons present to create a more than positive accuse.
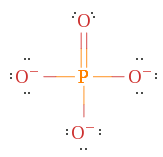
Example 1. PO4 iii-, Phosphate ion
With four oxygens present with 6 (6) electrons each and a phosphorus with five (v) in that location should be a total of 31 electrons. All the same, since at that place is a accuse of -3.
There are a few things to go along in heed. Phosphorus is in Period iii, which means it can hold more than 8 electrons and creates a double bond to the oxygen which fulfills the octet rule for i oxygen, but not the others.
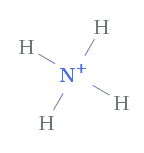
Case 2. NH4 + , Ammonium ion
With ammonium, nosotros are dealing with a positively charged polyatomic ion. The total valence electrons of the nitrogen and four hydrogens is 9 electrons. Since at that place is a positive accuse of ane+ that means there is one less electron, so there will exist a total of viii, which are represented by the four bonds as lines.
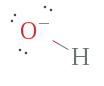
Instance 3. OH–, Hydroxide ion
The hydroxide ion has a full of how many electrons? Well, oxygen has vi and hydrogen has 1, but since there is a negative charge on the ion, information technology will have an additional ion making a full viii electrons, which are representing by the bonding pair between oxygen and hydrogen along with the three nonbonding (lone) pairs surrounding oxygen.
Central Concepts:
Determine the total number of valence electrons of the element or compound. If a molecule has more than one element, add together the valence electron of all elements present in the compound.
Make up one's mind which atom volition be the key atom of the Lewis Dot Structure. The central atom is the to the lowest degree most electronegative atom in the compound. Recall the trend for electronegativity on the periodic table. One time determined, draw that element by diminutive symbol in the center and depict unmarried bonds to the other atoms.
Subtract full beat of valence electrons (2 for H, eight for everything else) of each outer atom from the full number of valence electrons associated with the molecule. Distribute the remaining electrons to the central atom as non-bonding pairs
Form double and triple bonds until the primal atom has a full octet.
Draw nonbonding pairs around the outer atoms until they have a full octet.
Check your work: Ensure that all of your valence electrons and bonds are accounted for.
Do with Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
- Carbon
- Sodium
- Neon
- HCl
- H2O
- SOtwo
- NO3 –
- ClOiii –
- CN–
- SOfour 2-
Looking for Chemistry do?
Check out our other articles on Chemistry.
You can also notice thousands of practice questions on Albert.io. Albert.io lets yous customize your learning feel to target practice where yous demand the most assist. Nosotros'll give you challenging practice questions to assist you achieve mastery in Chemistry.
Start practicing here .
Are you a teacher or administrator interested in boosting Chemistry pupil outcomes?
Larn more about our schoolhouse licenses here.
cervantezmarsureend.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.albert.io/blog/how-to-draw-lewis-structures/
0 Response to "how to draw 3d structures"
Enregistrer un commentaire